ঠিকানা
বাংলাদেশ ফার্টিলিটি হাসপাতাল লিঃ ই ব্লক, মেইন রোড, বনশ্রী, রামপুরা ঢাকা ( বনশ্রী আইডিয়াল স্কুল থেকে ১০০ মিটার পূর্বে)
Book an appointment
০১৯৭৫০০৯৭৯৬
বাংলাদেশ ফার্টিলিটি হাসপাতাল লিঃ ই ব্লক, মেইন রোড, বনশ্রী, রামপুরা ঢাকা ( বনশ্রী আইডিয়াল স্কুল থেকে ১০০ মিটার পূর্বে)
০১৯৭৫০০৯৭৯৬
বাংলাদেশ ফার্টিলিটি হাসপাতাল লিঃ ই ব্লক, মেইন রোড, বনশ্রী, রামপুরা ঢাকা ( বনশ্রী আইডিয়াল স্কুল থেকে ১০০ মিটার পূর্বে)
০১৯৭৫০০৯৭৯৬
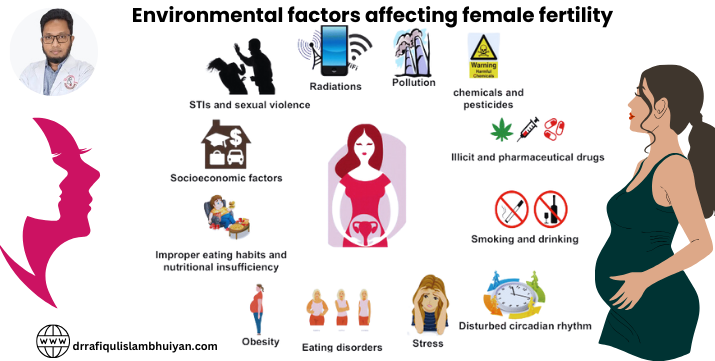
Environmental factors affecting female fertility can significantly impact female fertility by influencing hormonal balance, egg development, and the overall reproductive process. Some of the environmental factors that may affect female fertility include:
It’s important to note that the impact of these factors can vary from person to person, and not all individuals will experience fertility issues due to environmental exposures. However, for couples struggling with fertility, it may be beneficial to assess and minimize exposure to potentially harmful environmental factors. Consulting with a healthcare provider or fertility specialist can help determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances.
©2024.Dr. Md Rafiqul Islam Bhuiyan. All Rights Reserved.